Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). MCQs are the most commonly used assessment format worldwide. They are a regular part of educational and professional settings, offering a versatile way to evaluate and test your knowledge.
If you’re a student getting ready for tests, an educator seeking effective assessment methods, or simply curious about the inner workings of MCQs, this guide is designed to be your go-to resource. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of MCQs, enabling you to approach them with confidence and decode their underlying mechanics. Let’s start learning about MCQs!
Additionally, to enhance your exam preparation, explore MCQs for Exams – a valuable resource providing subject-wise and topic-wise sample MCQs. These practice questions are designed to improve your understanding of multiple-choice questions and boost your exam readiness effectively.
What are MCQs?
MCQ or MCQs is a commonly used abbreviation for “Multiple Choice Questions” around the world. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) are a form of test or quiz question that offers multiple choices, typically including one accurate answer and various incorrect ones. Your task is to select the correct response from the given options. MCQs serve as a way to evaluate your knowledge, grasp of concepts, and ability to make informed decisions across various subjects and areas. Widely employed in education, assessments, and evaluations, they provide a means to gauge your familiarity with a subject matter. MCQs are commonly used in aptitude tests, IQ assessments, and personality evaluations.
Additionally, Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) play a crucial role in surveys and questionnaires, offering an organized method to gather insights and opinions from respondents. Whether in market research, social studies, or scientific investigations, MCQs simplify data collection by providing predefined response options. This standardized approach streamlines analysis and ensures reliable data, facilitating informed decision-making across diverse fields.
History of Multiple-Choice Questions
The history of Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) dates back to 1914 when educational psychologist Frederick J. Kelly introduced the concept. He designed them as a practical way to score exams more efficiently. Over time, MCQs gained popularity due to their ability to assess a broad range of content and provide objective grading. Today, they are a widely used assessment format in education, professional settings, and various online platforms.
Components of Multiple-Choice Questions
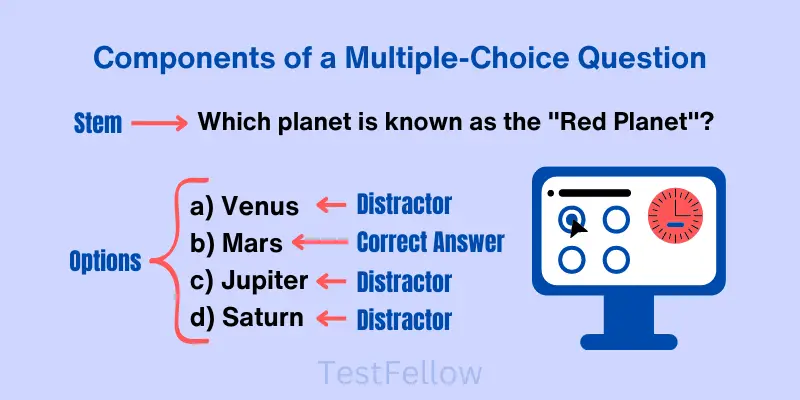
Multiple-choice questions (MCQs) consist of a stem, options or choices, correct answer(s), and distractors. Breaking down an MCQ into its individual parts can help you approach these questions more effectively.
1. Question Stem:
This is the main part of the MCQ that presents the problem or question you need to answer. It provides context and sets the stage for the choices that follow.
2. Options or Choices:
MCQs offer a set of options from which you must choose the correct answer. These choices are carefully crafted to challenge your knowledge and comprehension.
3. Correct Answer:
Among the options, one is the correct answer. Your task is to identify this accurate choice based on your understanding of the question.
4. Incorrect Answers (Distractors):
Distractors in multiple-choice questions are cleverly crafted incorrect answers meant to challenge your thinking. They’re designed to encourage careful consideration and smart choices. Even though distractors might seem correct, they’re actually wrong. They’re used to test how well you truly grasp the subject and can separate truth from falsehood. Their main role is to see if you can tell what’s real and what’s not.
Understanding these different components will enhance your ability to tackle MCQs effectively and boost your success in assessments and exams.
Types of MCQs with Examples
Multiple-choice questions (MCQs) come in various types, each serving a distinct purpose in assessing your knowledge and understanding. Let’s explore these 24 types along with illustrative examples to help you grasp their formats and applications. If you’re looking for guidance on how to answer multiple-choice questions, we’ve got you covered!”
1. Single-Answer MCQs
Single-Answer MCQs pose a question alongside several options, with just one being correct. These questions assess your capacity to discern the precise answer from the provided choices. Such MCQs focus on evaluating your ability to make accurate selections, compelling you to navigate through potential distractors and choose the most fitting response. They are a fundamental tool in testing your knowledge, comprehension, and analytical skills across various subjects and assessments. Mastering single-answer MCQs involves not only understanding the content but also honing your ability to make informed decisions within a limited context.
Example Question:
Which planet is known as the “Red Planet”?
a) Venus
b) Mars (Correct Answer)
c) Jupiter
d) Saturn
2. Multiple-Answer MCQs
Multiple-Answer MCQs introduce a different challenge by presenting a question along with options, where more than one answer can be correct. These questions gauge your ability to identify all accurate choices within a specific context. They require a deeper understanding of the subject matter, as you must discern multiple correct responses while also differentiating them from distractors. Excelling in multiple-answer MCQs demonstrates your grasp of nuanced concepts and your skill in differentiating between valid and incorrect choices. This type of MCQ adds complexity to assessments, testing not only your knowledge but also your precision in selecting multiple correct solutions to reflect a comprehensive understanding.
Example Question:
Which of the following are primary colors?
a) Red (Correct Answer)
b) Yellow
c) Green (Correct Answer)
d) Purple
e) Blue (Correct Answer)
f) Black
3. True/False MCQs
True/False MCQs center on statements that you classify as either true or false. These questions serve as a tool to evaluate your grasp of particular facts or concepts. With a binary nature, True/False MCQs prompt you to analyze the accuracy of provided statements, reinforcing your comprehension of fundamental information. While seemingly straightforward, these MCQs demand careful consideration, as they test your ability to differentiate between accurate and incorrect statements.
Excelling in True/False MCQs requires not only factual knowledge but also the ability to critically evaluate information, making them an essential component of assessments that assess both rote understanding and critical thinking skills.
Example Question:
Is the following statement true or false?
Water boils at 100°C.
a) True (Correct Answer)
b) False
4. Yes/No MCQs
A Yes or No MCQ is a simple format where a statement or question is presented, and respondents have the choice of answering either “Yes” or “No”. This type of question is easy to understand and quick to answer, making it suitable for gathering straightforward opinions or facts. This format is often used to obtain quick and clear responses from participants.
Example Question:
Is the Earth round?
a) Yes (Correct Answer)
b) No
5. Odd One Out MCQs
The Odd One Out Multiple Choice Question (MCQ) challenges respondents to identify an item that doesn’t fit with the rest in a given group. By presenting a collection of items, this format evaluates the participant’s capacity to detect variations and patterns among them. This type of question encourages critical thinking and observation skills as respondents analyze the items to pinpoint the one that deviates from the expected pattern or category. It’s a creative way to assess cognitive abilities related to identifying distinctions within a set of options.
Example Question:
Which of these is the odd one out?
a) Apple
b) Banana
c) Orange
d) Carrot (Correct Answer)
6. Best Answer MCQ
In a “best answer MCQ”, respondents are presented with a list of choices and are tasked with selecting the option that best fits the provided context or is most accurate. This format aims to evaluate a participant’s ability to critically analyze the options and discern the most suitable response based on the given information. It encourages respondents to apply their understanding and judgment to identify the option that aligns most effectively with the question’s requirements.
Example Question:
Choose the best answer:
Which study method is most effective?
a) Studying briefly before a test
b) Regularly Studying (Best Answer)
c) Studying only important questions
d) Cramming all night before an exam
7. Matching Type MCQs
Matching Type MCQs present a unique challenge where you’re tasked with creating meaningful pairs by linking items from two separate columns. This type of question assesses your aptitude for establishing logical relationships and connections between distinct elements. By requiring you to identify correlations and linkages, matching MCQs evaluate your ability to discern patterns, draw associations, and comprehend the interplay between different pieces of information.
Excelling in this category showcases your proficiency in recognizing relationships, making it a valuable skill in subjects that demand analytical thinking and the ability to synthesize information cohesively.

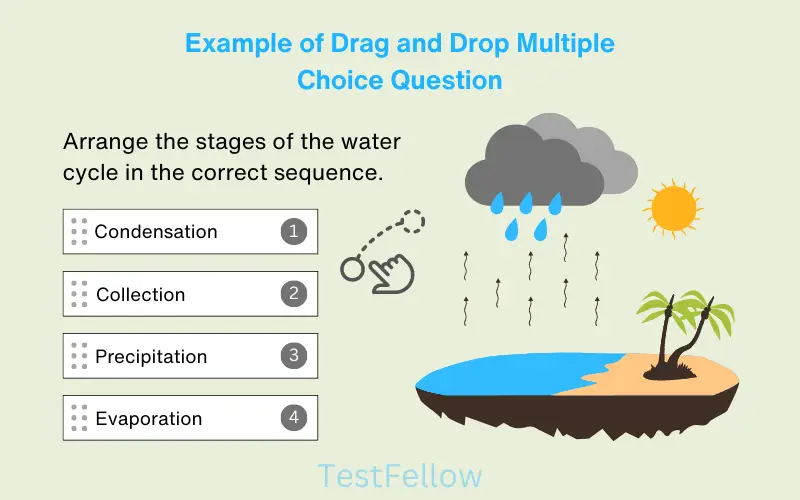
8. Drag and Drop MCQ
Drag and Drop Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) add an engaging twist to traditional assessments. In this format, you’re provided with a set of options that you can literally move around the screen—dragging and dropping them into their appropriate positions. This dynamic interaction challenges you to match choices accurately to their respective contexts, effectively evaluating your ability to establish connections and make informed selections.
9. Drop Down Menu MCQs
Drop-down Menu MCQs present a question with answer options that appear in a dropdown list. In this format, you select the correct answer from the available choices, utilizing a concise and organized display for multiple options. This user-friendly format simplifies the presentation of choices, eliminating clutter and ensuring a seamless interaction.

10. Star Rating MCQs
Star Rating Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) employ a familiar rating system, often depicted as stars, to gauge your evaluation of different options. This format proves valuable for assessing preferences or qualities on a graduated scale. By assigning stars to each choice, you express your judgment of factors like importance, difficulty, or satisfaction, providing a nuanced way to quantify subjective attributes.
Star Rating MCQs are particularly effective when a quantitative measure is required, allowing learners to communicate their opinions with precision and enabling educators to gather insights into nuanced preferences or perceptions.

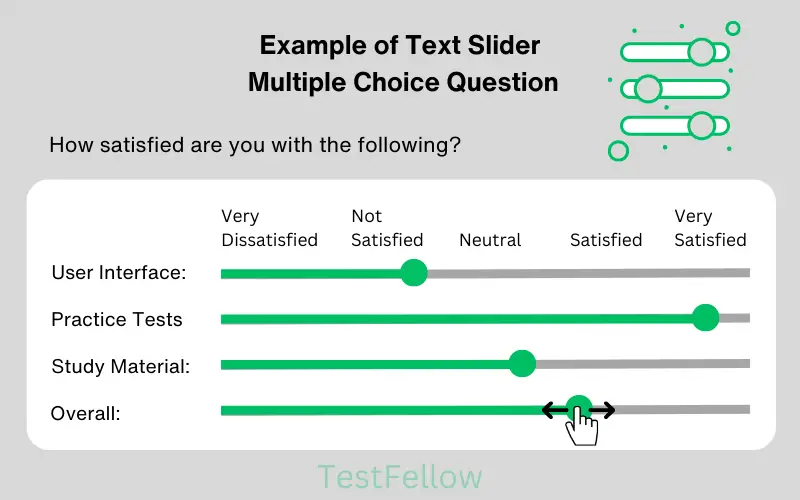
11. Text Slider MCQ
An excellent substitute for open-ended questions, Text Slider MCQs offer an interactive twist. They present a scale with text-based choices, allowing you to slide the marker and share preferences, opinions, or evaluations within a defined range. This dynamic method empowers users to provide detailed responses that match their viewpoints with precision. Text Slider MCQs enhance evaluation by providing versatile feedback options, enabling users to precisely convey their thoughts while maintaining a user-friendly experience.
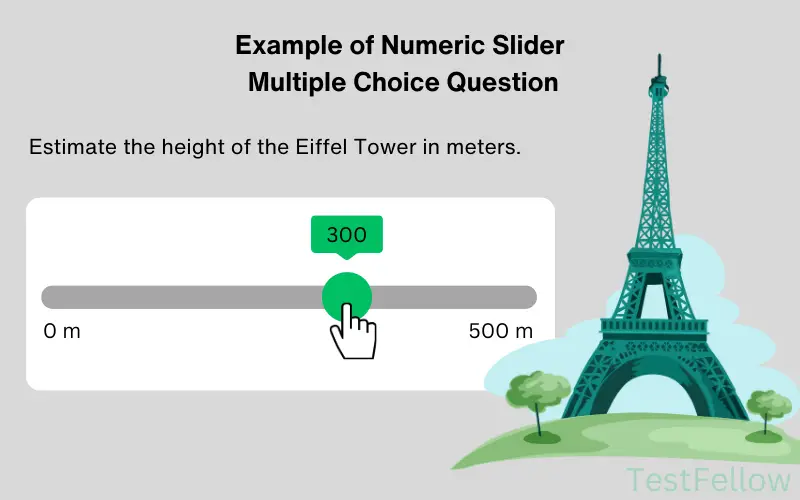
12. Numeric Slider MCQs
Numeric Slider MCQs offer an interactive twist, featuring a sliding scale with numeric choices. Users adjust the slider to select a numerical value that aligns with the context provided. This dynamic format empowers participants to quantitatively express their preferences, estimates, or judgments.
This type of MCQs enrich assessment by enabling precise quantification within a user-friendly interface, promoting engagement, and enhancing the depth of responses across various numerical contexts.
13. Push to Social Media MCQs
Push to Social MCQs add an interactive dimension by prompting users to share their responses on social media. This innovative approach sparks engagement and conversations related to the question’s theme, cultivating a collaborative learning space.
For instance, when asked about historical figures, users can push their choice to Twitter and invite friends to participate. This format not only enhances individual learning but also extends the educational experience to online communities, promoting insightful discussions and diverse perspectives through interactive sharing.
14. Thumbs Up/Down MCQs
Thumbs Up/Down MCQs offer a simple binary choice using thumbs-up and thumbs-down icons. You indicate your agreement or disagreement with a statement. The choices essentially comprise an icon or image representing thumbs up or thumbs down, which assists in describing the rating choice. It helps people quickly decide if they like or don’t like something.

15. Smiley Rating MCQ
Smiley Rating MCQs infuse assessments with emotive expressions, employing smiley faces to convey varying degrees of sentiment or preference. Respondents select the smiley that resonates with their viewpoint, enriching responses with emotional context.
This format not only quantifies opinions but also integrates feelings into learning. Smiley Rating MCQs foster engagement by offering an intuitive, visually appealing interface that enables participants to communicate sentiments effectively and contribute depth to their feedback.

16. Matrix Table Multiple Choice Question
In this type, respondents are presented with a table consisting of rows and columns. Each row represents a specific item or statement, while each column represents different options or levels of agreement, importance, etc. Respondents are required to choose one option from each row. This format is useful for assessing multiple variables or preferences simultaneously.
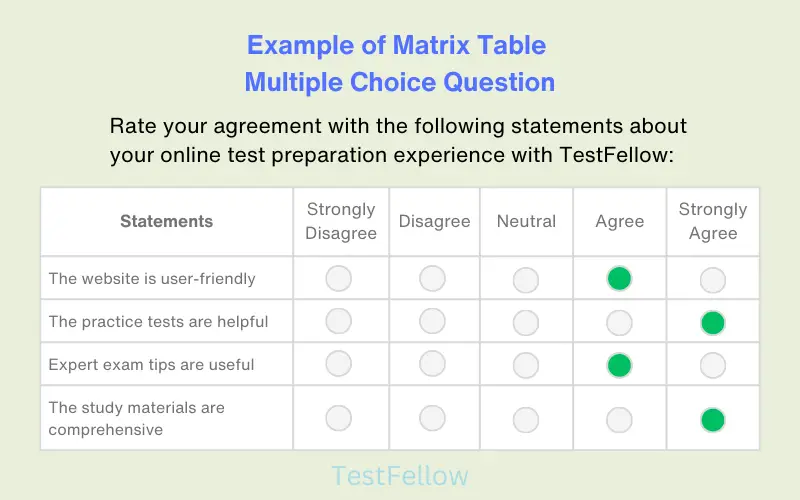
17. Multi Point Scale Matrix Table MCQs
This type is similar to the Matrix Table MCQs, but it allows respondents to select multiple options from each row instead of just one. This allows for a more nuanced response, as respondents can indicate varying levels of agreement or preference for each item.
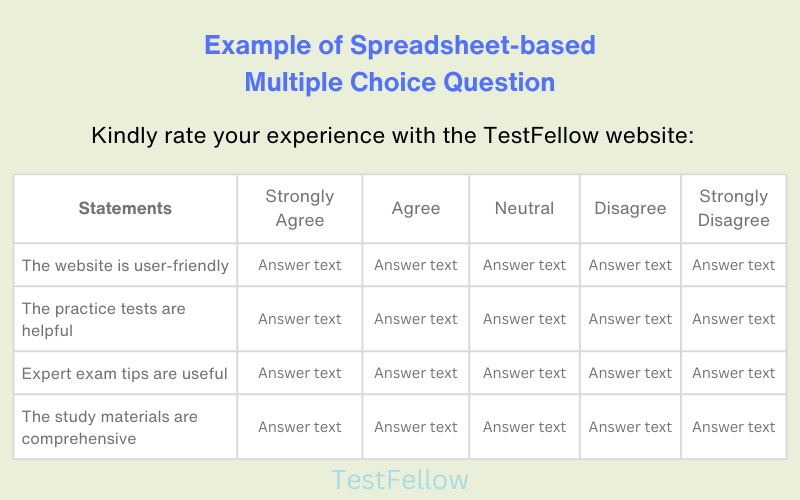
18. Spreadsheet-based MCQs
Spreadsheet-based MCQs employ a spreadsheet-like interface, enabling participants to interact with cells housing text box options. This setup is apt for situations demanding calculations, comparisons, or data manipulations. These types of questions enable respondents to input text explaining their chosen answer. Typically, these choices span the spectrum from ‘extremely like’ to ‘extremely dislike,’ accompanied by reasons for their preference and possible suggestions.
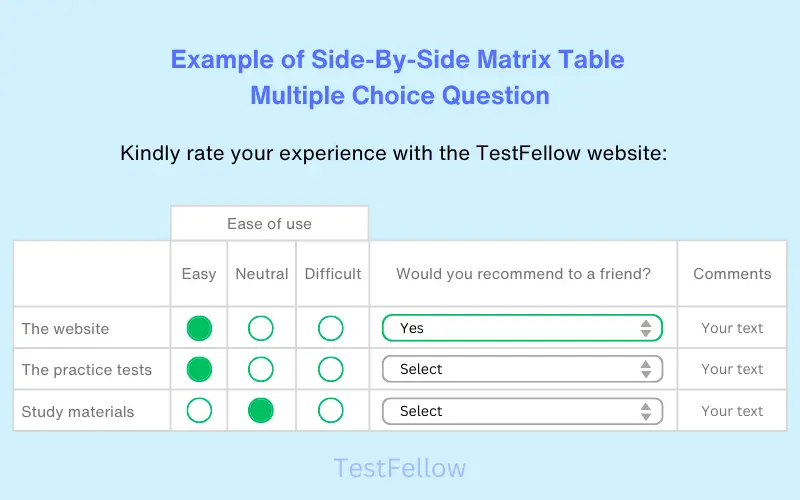
19. Side-By-Side Matrix Table MCQ
The Side-by-Side Matrix Table Multiple Choice Question is a powerful tool for condensing multiple questions into a single table. Within this format, every column becomes an independent question, complete with its structure, format, and options. Each row corresponds to an item, and respondents address these side-by-side inquiries accordingly. This approach streamlines the assessment process, making it efficient and informative.
20. Rank Order Multiple Choice Question
The Rank Order question type offers respondents a distinctive chance to arrange a group of items in order of preference. For instance, in rank order scaling-based multiple-choice questions, a selection of brands or products can be ranked according to a specific quality. This ranking can be represented numerically using a dropdown box. When included in a survey, this question helps the creator grasp the respondent’s sequence of preference, offering insights into their choice priority.

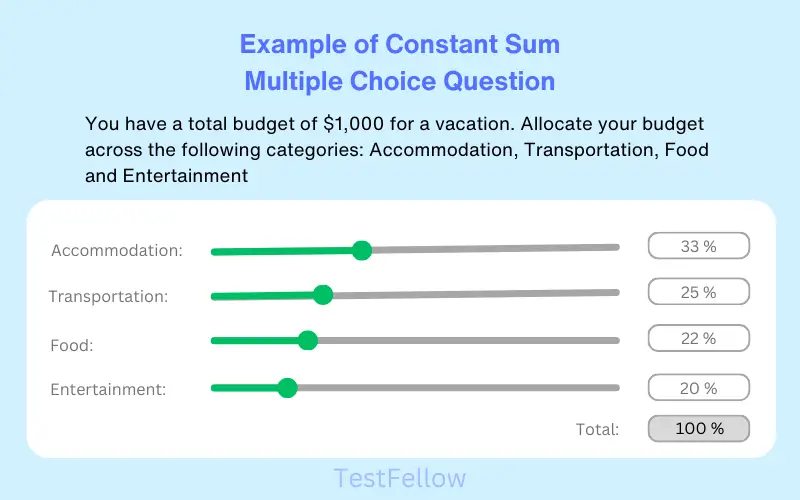
21. Constant Sum Multiple Choice Question
The Constant Sum multiple choice question structure assigns participants a specific sum of points for distribution among several choices, gauging their significance or relevance. This approach illuminates the hierarchy of priorities in a comparative manner. This question type empowers respondents to input numerical values across multiple variables, ensuring the total adds up to a predetermined sum. The cumulative value of these numeric entries can be showcased to the respondents. This type of question proves highly effective for inquiries concerning financial matters, budgeting, and percentage-based scenarios.
22. Single-Answer Image-Based MCQs:
Single Answer Image-Based MCQs combine the visual aspect with the traditional multiple-choice format. Here, radio buttons are utilized to facilitate your selection of the correct answer based on the visual provided. In these questions, an image or diagram is presented alongside options, where you must select the one correct answer based on the visual content provided.
This type of MCQ evaluates your ability to interpret visual information and apply it to the question’s context. By analyzing images, charts, or diagrams, you demonstrate your capacity to connect visual cues with the subject matter, fostering a holistic understanding. Excelling in these MCQs showcases your aptitude for visual learning and critical thinking, proving valuable in fields that require visual analysis and comprehension.

23. Multiple Answer Image-Based MCQs
Multiple Answer Image-Based MCQs operate much like Single Answer Image-Based MCQs, but the key difference is that you’re allowed to select more than one image option. In this format, an image or diagram accompanies response options, creating an engaging learning experience. Notably, checkboxes are employed to enable you to choose multiple correct answers based on the visual content provided. These MCQs assess your ability to interpret visual information, recognize patterns, and apply them to the context of the question.

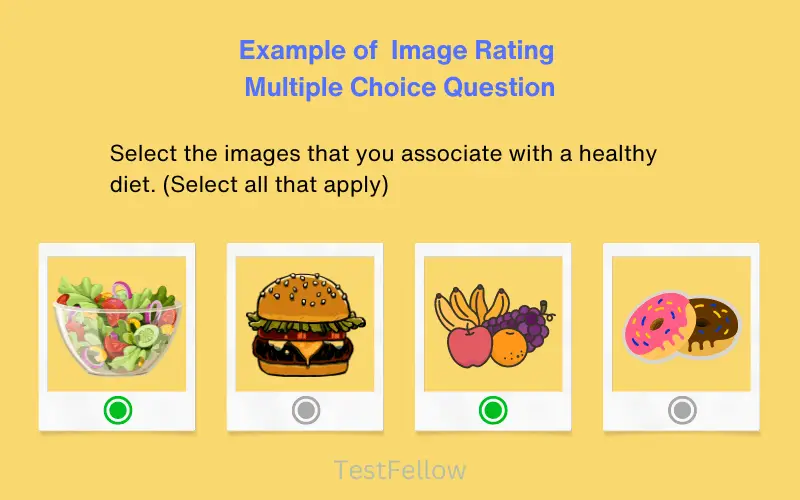
24. Image Rating MCQs
An image rating question falls under the umbrella of close-ended questions. It presents respondents with a range of image-based options, from which they select single or multiple images that resonate the most with them. Similar to other multiple-choice questions, the distinction here lies in the format—options are visual representations. The primary aim of image rating questions is to captivate respondents and provide a deeper comprehension of each option’s essence. These questions, presented in visual form, serve to actively involve participants and offer a more vivid understanding of the choices at hand.
Each of these creative MCQ formats adds an interactive and engaging element to the assessment process, catering to various learning preferences and enhancing your understanding of the subject matter.
Advantages of Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) are widely used in the educational sector and workplaces due to their numerous benefits. These question formats offer a range of advantages that contribute to their widespread use and popularity. In this section, we’ll explore five of the most significant benefits that MCQs bring to the table.
1. Efficient Assessment
MCQs enable efficient evaluation of a wide range of content within a relatively short time. Educators and examiners can cover a diverse array of topics and concepts in a single assessment, allowing for comprehensive testing of knowledge.
2. Objective Evaluation
The objective nature of MCQs reduces subjectivity in grading. Since there’s a clear right answer for each question, grading is consistent and eliminates potential bias or interpretation discrepancies.
3. Quick Feedback
MCQ assessments offer swift feedback to both learners and educators. With automated grading systems, learners can promptly identify areas of strength and weakness, while educators can adjust their teaching strategies accordingly.
4. Assessing Diverse Cognitive Levels
MCQs can be crafted to assess various cognitive levels, from basic recall of facts to higher-order thinking skills like analysis and application. This versatility allows educators to gauge a broad spectrum of learning outcomes.
5. Higher Response Rates and Increased Participation
One of the significant advantages of employing Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) is the potential for higher response rates and increased participation. Due to their structured and concise format, MCQs are often perceived as less time-consuming as compared to open ended questions, encouraging a larger number of individuals to engage with the assessment or survey. This uptick in participation is particularly beneficial in educational settings, where teachers can gauge student understanding effectively.
Moreover, in business contexts, the higher response rates translate to more comprehensive insights from customers or stakeholders, enabling organizations to make well-informed decisions based on a broader range of perspectives.
Incorporating MCQs into assessments and educational materials offers a range of advantages that streamline the learning process and promote effective evaluation.
Disadvantages of Multiple Choice Questions
The advantages associated with Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) are undeniably significant. However, it is equally crucial to recognize the limitations that accompany their application. In this section, we’ll explore MCQs’ disadvantages, highlighting areas where they might not fully serve as effective assessment tools.
1. Limited Depth of Understanding
While MCQs are useful for assessing factual knowledge, they might not effectively capture the depth of a student’s understanding. These questions often present options that require recall rather than analysis. In subjects where complex concepts and critical thinking are crucial, MCQs may fall short in evaluating a student’s ability to grasp intricate connections and apply knowledge in practical scenarios.
2. Guessing and Chance
MCQs, especially those with multiple choices, can accidentally reward lucky guesses. Respondents might select an option based on partial knowledge or eliminate obviously incorrect choices, potentially leading to inflated scores that do not truly reflect their expertise. This element of chance could undermine the accuracy of the assessment and blur the distinction between knowledgeable respondents and those who merely guessed right.
3. Narrow Assessment Scope
Due to the limited format of MCQs, they might not cover the full spectrum of a topic. This could result in overlooking crucial nuances and aspects of understanding. For subjects requiring a holistic comprehension or interdisciplinary connections, MCQs might inadvertently prioritize certain aspects while neglecting others, thus providing an incomplete picture of a student’s overall knowledge.
4. Avoiding Critical Thinking
MCQs, often designed to have clear-cut answers, might encourage memorization of facts rather than the application of critical thinking skills. Students might focus on memorizing options rather than engaging in analytical reasoning or problem-solving. In the real world, where ambiguity and complex situations are common, the absence of critical thinking assessment could hinder a student’s ability to tackle unfamiliar challenges effectively.
Conclusion
With this expansive exploration of 24 diverse MCQ types complemented by illustrative examples and insights into their advantages and disadvantages, you have delved deep into the world of multiple-choice questions. Armed with this comprehensive insight, you’re empowered to navigate the intricacies of MCQs with confidence, applying your newfound knowledge to assessments, evaluations, and learning scenarios. Your enriched understanding of this versatile format equips you to approach various subjects and situations with a heightened sense of comprehension and adeptness. Whether you’re preparing for exams, job tests, or online assessments, you can now navigate them with assured confidence.
FAQs about Multiple Choice Questions
1. Who invented the MCQs?
The invention of MCQs is attributed to Frederick J. Kelly, an American educational psychologist. He introduced the concept in 1914 as a way to efficiently score large numbers of exams. The format gained popularity due to its effectiveness in assessing a wide range of content and providing objective grading.
2. What does MCQ stand for?
MCQ or MCQs stands for Multiple Choice Question. It’s an abbreviation commonly used to refer to a type of objective assessment where respondents choose the most appropriate answer from a list of options. This format is also known as multiple choice (MC) or objective response.
3. What is the purpose of MCQs test?
The purpose of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) tests is to assess a person’s understanding and knowledge of a particular subject or topic. MCQs present a question along with several answer choices, among which one or more are correct. MCQs assess various cognitive skills, from basic recall to critical thinking. Their structured setup enables effective assessment across content areas, valuable for educators, employers, and learners for informed choices.
4. Can practical skills be assessed with MCQs?
Yes, practical skills can be evaluated through scenario-based MCQs. These questions present real-life situations, allowing test-takers to apply their knowledge to practical scenarios. For example, a nursing exam might include a scenario where students choose the most appropriate response for a patient’s specific condition, assessing their ability to apply medical knowledge in a realistic context.
5. How do MCQs aid learning?
MCQs aid learning by encouraging active recall and engagement. When answering MCQs, learners retrieve information from memory, reinforcing their understanding of the material. Additionally, MCQs prompt critical thinking as they require analyzing options to identify the correct answer. This interactive approach promotes deeper comprehension and retention of concepts.
6. Why are there different types of multiple-choice questions?
The existence of different types of multiple-choice questions serves to cater to various learning styles, subject matters, and assessment objectives. Each type emphasizes different skills and cognitive abilities. For instance, image-based MCQs evaluate visual interpretation skills, while text slider MCQs assess nuanced preferences. Having different types helps teachers and testers understand many aspects of how well someone understands, thinks, and uses what they’ve learned, which makes tests better suited to each person.
Related Articles:
- What Are Assessments? 14 Types with Examples
- A Comprehensive Guide to 23 Types of Questions
- What Is a Psychometric Test – A Comprehensive Guide
- What is an IQ Test – A Comprehensive Guide
- What are Personality Tests – A Comprehensive Guide
- What are Aptitude Tests – A Comprehensive Guide
- What is a Test? 10 Types of Tests in Education
- Top 10 Tips to Prepare for a Psychometric Test
- How to Pass an Aptitude Test: Top 10 Effective Tips
- How to Prepare for Personality Tests: 10 Expert Tips
- How to Answer Multiple Choice Questions: 10 Tips

